Comprehensive eye examination in Greater Noida
Our Services
-
comprehensive eye examination
-
cataract assessment & Microincision Surgery
-
computerised testing for glasses
-
Glaucoma Care
-
pediatric eye care
-
retina checkup
-
diabetic retinopathy screening
-
intra ocular (Eye) pressure testing
-
retinopathy of prematurity screening
-
amblyopia therapy / lazy eye therapy
-
treatment for dryness, allergies, infection of eye
-
Phacoemulsification
-
Small incision cataract surgery (SICS)
-
Pterygium excision
-
Pediatric cataract
-
Pediatric oculoplasty
-
Squint
-
Phaco-trabeculectomy
comprehensive eye examination
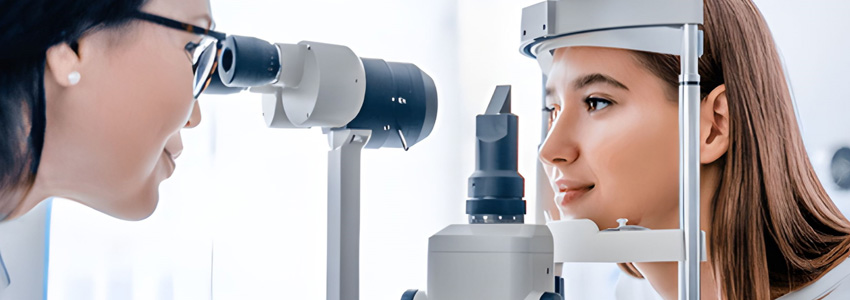
A comprehensive eye examination is a thorough assessment of the eyes and visual system. It involves a series of tests and assessments to check for vision problems, eye diseases, and overall eye health.
Components of a Comprehensive Eye Examination
- Medical History Review: The doctor will ask about your general health, family history of eye diseases, medications, and any vision problems you might be experiencing.
- Visual Acuity Test: This measures how clearly you can see at different distances. You'll be asked to read letters on a chart (Snellen chart) from a distance.
- Refraction Assessment: This determines your exact eyeglass prescription. The doctor uses a phoropter to show you different lens options and find the combination that gives you the clearest vision.
- Pupil Dilation: Eye drops are used to dilate (widen) your pupils, allowing the doctor to see the back of your eye more clearly. This helps in examining the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels for any signs of disease.
- Tonometry: This test measures the pressure inside your eyes (intraocular pressure) to check for glaucoma, a condition that can damage the optic nerve.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: Using a special microscope, the doctor examines the structures at the front of the eye, including the cornea, iris, lens, and anterior chamber, to detect abnormalities or diseases.
- Retinal Examination: With your pupils dilated, the doctor uses an ophthalmoscope or a retinal camera to examine the retina, optic disc, and blood vessels at the back of the eye.
- Visual Field Test: This assesses your peripheral (side) vision to detect blind spots and other vision abnormalities, which can be signs of glaucoma or neurological conditions.
- Color Vision Testing: This evaluates your ability to distinguish colors, which can reveal color blindness or other vision issues.
- Binocular Vision Assessment: This checks how well your eyes work together (eye teaming) and can detect problems like strabismus (crossed eyes) or amblyopia (lazy eye).
- Depth Perception Test: This evaluates your ability to perceive the distance and depth of objects.
Benefits of a Comprehensive Eye Examination
- Early Detection of Eye Diseases: Many eye diseases, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy, have no early symptoms. A comprehensive eye exam can detect these conditions early, allowing for prompt treatment and better outcomes.
- Vision Correction: Identifies refractive errors like nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism, ensuring you get the correct prescription for glasses or contact lenses to improve your vision.
- Overall Health Monitoring: Eye exams can reveal signs of systemic health issues like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. The eyes can reflect changes in overall health, and early detection can lead to better management of these conditions.
- Prevention of Vision Loss: Early detection and treatment of eye diseases can prevent or slow down vision loss, preserving your quality of life.
- Customized Eye Care: Provides personalized recommendations for eye care, including the need for protective eyewear, management of chronic conditions, and lifestyle modifications to maintain healthy vision.
- Children’s Eye Health: Regular eye exams are crucial for children to ensure proper vision development, detect vision problems that can affect learning and development, and prescribe corrective measures if needed.
- Aging Eye Health: As you age, your risk for eye diseases increases. Regular comprehensive eye exams help monitor changes in your vision and eye health, ensuring timely intervention.
Regular comprehensive eye examinations are essential for maintaining good eye health and overall well-being. They provide early detection of potential issues, offer corrective solutions, and help monitor systemic health conditions that can affect your eyes.